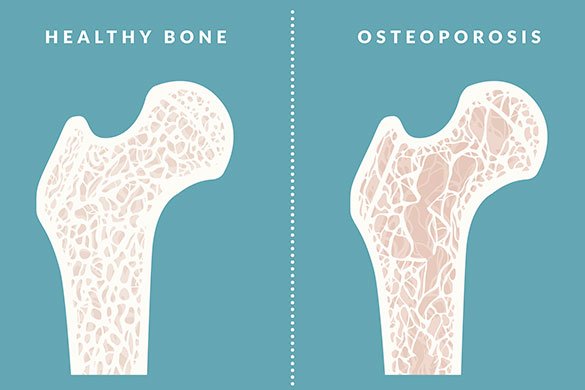
Osteoporosis weakens bones to the point that they can break easily. It is called a “silent disease” because people who develop it may not notice any changes until a bone breaks usually a bone in the hip, spine, or wrist. Bones are made of living tissue.
Osteoporosis causes bones to become weak and brittle so brittle that a fall or even mild stresses such as bending over or coughing can cause a fracture. Osteoporosis-related fractures most commonly occur in the hip, wrist or spine.
Osteoporosis affects men and women of all races. But white and Asian women, especially older women who are past menopause, are at highest risk. Medications, healthy diet and weight-bearing exercise can help prevent bone loss or strengthen already weak bones.
Symptoms
There typically are no symptoms in the early stages of bone loss. But once your bones have been weakened by osteoporosis, you might have signs and symptoms that include:
- Back pain, caused by a fractured or collapsed vertebra
- Loss of height over time
- A stooped posture
- A bone that breaks much more easily than expected
Prevention
Good nutrition and regular exercise are essential for keeping your bones healthy throughout your life.
Calcium
Men and women between the ages of 18 and 50 need 1,000 milligrams of calcium a day. This daily amount increases to 1,200 milligrams when women turn 50 and men turn 70.
Good sources of calcium include:
- Low-fat dairy products
- Dark green leafy vegetables
- Canned salmon or sardines with bones
- Soy products, such as tofu
- Calcium-fortified cereals and orange juice
Vitamin D
Vitamin D improves the body’s ability to absorb calcium and improves bone health in other ways. People can get some of their vitamin D from sunlight, but this might not be a good source if you live in a high latitude, if you’re housebound, or if you regularly use sunscreen or avoid the sun because of the risk of skin cancer.
Dietary sources of vitamin D include cod liver oil, trout and salmon. Many types of milk and cereal have been fortified with vitamin D.
Exercise
Exercise can help you build strong bones and slow bone loss. Exercise will benefit your bones no matter when you start, but you’ll gain the most benefits if you start exercising regularly when you’re young and continue to exercise throughout your life.
Combine strength training exercises with weight-bearing and balance exercises. Strength training helps strengthen muscles and bones in your arms and upper spine. Weight-bearing exercises such as walking, jogging, running, stair climbing, skipping rope, skiing and impact-producing sports affect mainly the bones in your legs, hips and lower spine.










